what can cause coaxle splitters to go bad
The following article discusses Coaxial cablevision splitters and addresses mutual questions on how the CableIQ can exist used to evaluate the cabling organisation with coax splitters.
Quick questions:
- Will CableIQ discover coax splitters? Yeah
- Volition CableIQ locate coaxial cable splitters? May be, please read the commodity below in full.
- Will the CableIQ Identifiers piece of work through a coax splitter? Click hither
- Can I tell how many times the signal is split? Click here
What are Coax Splitters?
Coax splitters are used in video transmissions systems to have a single video feed and branch it off to multiple places. Coaxial cable splitters typically come in ii, 3, 4 and 6 mode configurations. Ideally, a coaxial cable splitter maintains the proper impedance environment on both the input and output ports. For video coax systems, this impedance is typically 75 ohms. As the proper noun implies, a coax indicate splitter takes the power on the input port and splits it every bit amid the output ports. For example, a 2-way splitter has ane input port and ii output ports. It sends half the power of the input signal to one of the output ports. The other half is sent to the other output port.
Is in that location a deviation in the quality of coax splitters?
Non all coax cable splitters are created equally. Low quality coax splitters can adversely affect the video signal, causing excessive attenuation of the signal (signal loss) and multiple reflections which tin cause ghosting (shadows on the moving-picture show). Figure 1 shows the departure in the construction between typical low and high quality two way splitters. The low quality splitter has a single ferrite which attempts to command the impedance of the splitter. This typically fails to produce a adept wideband impedance match and results in unwanted reflections and signal loss. The high quality splitter has a printed circuit with multiple components that assure the performance of the splitter over a wide frequency (preferred).
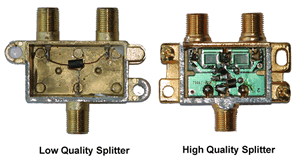
Effigy 1: Motion picture Comparison Low and High Quality Splitter Construction
Why do I care if there are splitters in the coax system?
It is often very useful to know whether at that place are splitters in a coax distribution organization and to be able to assess the splitter quality. Its also useful to decide how many times the signal is carve up on a specific run. Some installation practices simply allow at most a 2 way split, so determining if there are multiple splitters is very important.
Can the CableIQ observe the presence of splitters?
Yes, the CableIQ tin notice the presences of splitters in a coax organization, just non ever testify their location (output branches must exist un-terminated). In the by, detecting the presence of splitters, their quality and the number of splits has been very hard to do without specialized examination equipment. Notwithstanding, the technology implemented in the CableIQ now allows this information to easily be adamant. The CableIQ running in Coax Discover Mode can detect the presence of a splitter in a coax run and alert the user. Once a splitter has been detected, the user can inspect the COAX TDR Trace to look at the reflections on the coax run and determine other information. The TDR trace will contain information to mostly appraise the quality of the splitter and how many times information technology is dissever.
The CableIQ implements a TDR (Time Domain Reflectometry) like engineering that allows it to determine the location of impedance changes. TDR is like radar and signals reflect off each point where at that place is an impedance alter. If the impedance alter goes higher, for example an open circuit, the reflection is positive. If the modify in impedance is lower and then the reflection is negative. The size of the reflection is a function of the size of the impedance change. With this simple noesis, a user can view the TDR trace and determine if there are impedance mismatches due to a splitter and how many times a betoken is carve up.
Consider the following example of coax cabling which has a 2 style splitter being tested by a CableIQ (Effigy two). It has 3 branches of lengths L1, L2 and L3 respectively. L2 and L3 are continued to the output ports of the splitter and are united nations-terminated.
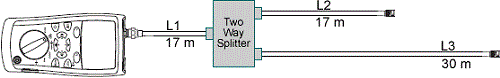
Figure 2: Example coax cabling test configuration with a splitter
When testing in Coax Discover Fashion, the CableIQ can discover the presence of the splitter. Effigy 3 shows the brandish with the Splitter or Fault warning that will be nowadays if the CableIQ suspects a splitter is in the cabling under test. This is the cue to the user that the Coax TDR trace should exist viewed for further information. The COAX Trace is accessed by pressing the F1 key.
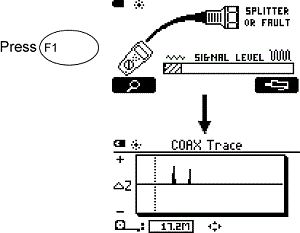
Figure 3: CableIQ Splitter Alarm and Coax Trace Screens
What will the COAX Trace bear witness if splitter is a high quality type?
An ideal or high quality splitter has the characteristic of looking like a 75 ohm impedance device across a wide frequency range on input and output ports. Therefore, when hooked into a 75 ohm cable system there will be footling to no reflection at the splitter since there isnt an impedance change. Only the reflections off the united nations-terminated ends of the output branches will be seen. There should be 1 and but one reflection for each branch. The reflections should occur at the sum of the length of the input and respective output branches. Figure 4 shows a representative COAX Trace for this condition.
Interpreting the information in the COAX Trace allows important conclusions to be drawn. In that location are simply two reflections. This is and indication the splitter is of good quality since there is no reflection for the splitter itself. The two reflections indicate that there is only a 2 way split. Note in the case of a good splitter the CableIQ may not be able to locate it since there is no reflection off a expert splitters, only it tin can detect there is a splitter in the cabling. However, sometimes even in the example of a good splitter there may exist a slight reflection that allows the user to decide the location of the splitter.
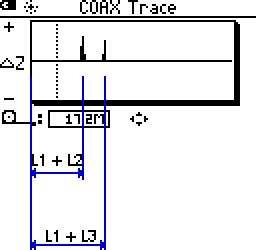
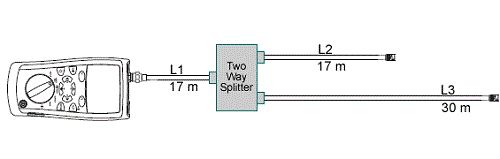
Figure 4: COAX Trace of high quality ii way splitter
What if the splitter is a low quality type?
Low quality splitters practice not provide a good wideband impedance friction match on all its ports and more often than not generate a low impedance reflection at the bespeak of the splitter. This will produce a negative reflection. Since the impedance match is not good, unexpected extra reflections may be seen on the COAX Trace. Figure five shows the COAX Trace for the case test setup when a low quality splitter is used.
This COAX Trace shows at that place is a large negative impedance change at the point of the splitter. This indicates the splitter is not a good impedance match. There are three reflections afterward the splitter, non two as in the instance of the good splitter. The first two reflections represent the ends of respective branches. The last one is due to some multi-reflection in the organization caused past the poor impedance match of the output ports. his splitter should be replaced. Since it produces a large reflection, information technology is easily located at virtually 17.2 k from the CableIQ.
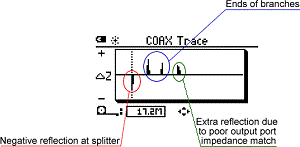
Effigy 5: COAX Trace with low quality ii manner splitter has more than ii reflections
Tin I tell how many times the indicate is split?
If there is a good quality splitter in the circuit, in that location should beane and only onepositive reflection corresponding to each un-terminated co-operative on the coax circuit. This is easily verified by viewing the COAX Trace. Figure vi shows an example where a 4 way splitter is seen in the circuit. In that location are 4 positive reflections in the COAX Trace.

Figure half-dozen: COAX Trace looking into iv mode splitter with united nations-terminated branches has 4 positive reflections.
Will the CableIQ Wire Map or Office ID Adapters work when there are splitters?
The ability for the adapters to work depends on the construction of the splitter. Most low quality splitters have a direct wire path from the input to output and the adapters volition generally function with these splitters in the circuit. Still, higher quality splitters (circuits) generally do not have a direct connection from the input to output. The connexion in these devices is generally through some form of transformer device which does not pass the signaling the CableIQ and adapter required to function. MultiMap adequacy is non supported in Coax mode, and so fifty-fifty if there are low quality splitters which take a direct connectedness, multiple adapters volition not been seen.
Make certain unused ports are terminated
For case, if you take a four port splitter and are simply using two of the output ports, the remaining two ports SHOULD be terminated. If not, expect to see a trace similar to that below:

Figure vii: COAX Trace looking into 4 way splitter with unused ports left united nations-terminated
Source: https://www.flukenetworks.com/knowledge-base/cableiq/coaxial-cable-splitters-cableiq
0 Response to "what can cause coaxle splitters to go bad"
Post a Comment